IT project life cycle
Are you a project manager in IT Services? Do you want to know what the project life cycle is for IT projects at York? Looking for standard document templates you can use? You're in the right place!
Project phases
We use six project phases to manage projects within IT Services at York.
It's important that the project sponsor approves the project's progress through each stage-gate.
It's the sponsor's responsibility to check that the project continues to deliver its objectives and remains aligned to the University's goals. They should also confirm that the project is ready for the next phase.
The diagram shows the project phases (in the middle) and the stage-gate checkpoints (on the right). On the left, it also shows how the project phases relate to the phases of change (plan, implement, embed).
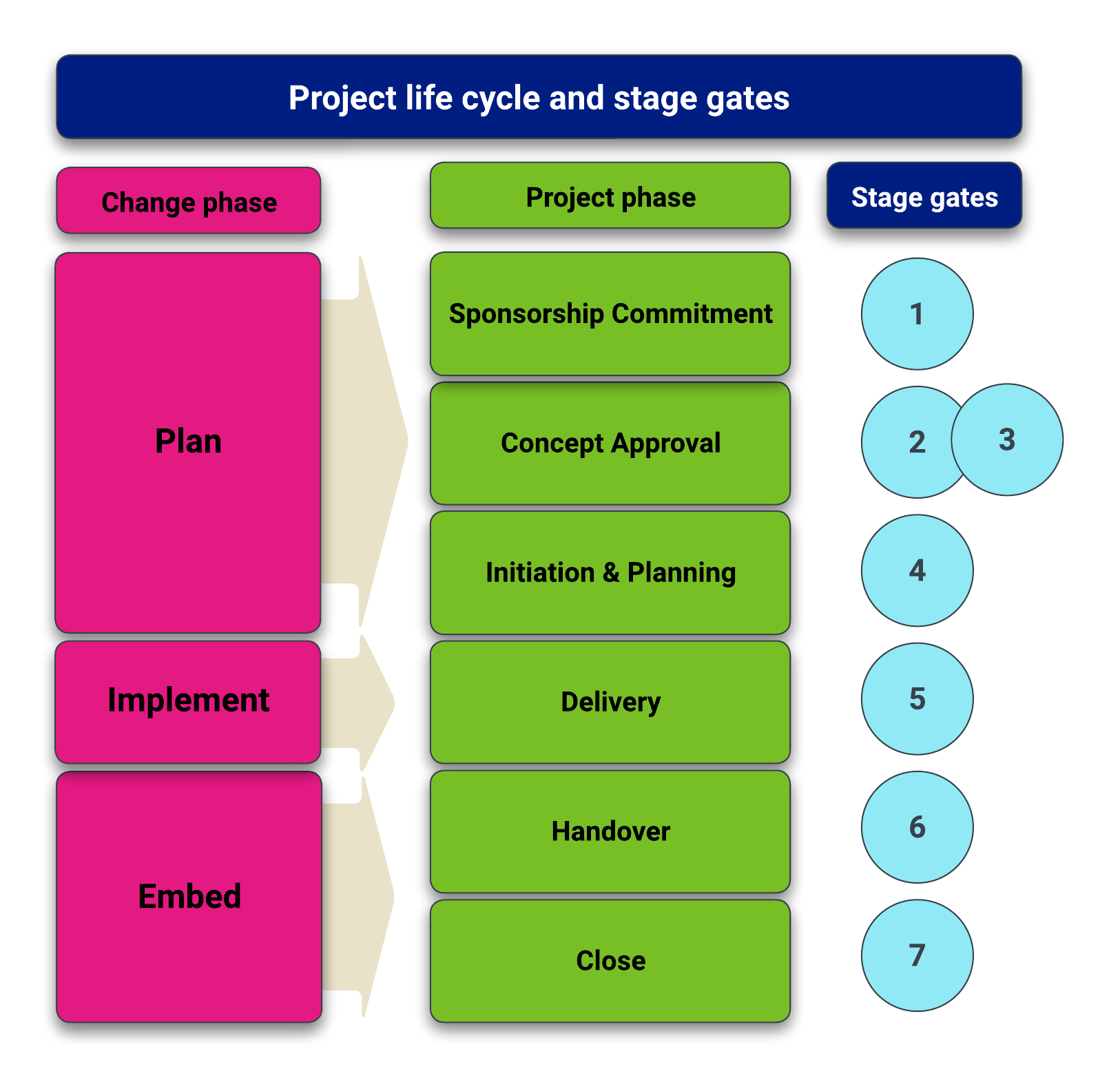
IT project life cycle and stage-gates diagram
Purpose
This phase assesses the level of sponsorship for a change. The project sponsor is accountable for the benefits that a project will bring and the reasons why the project is needed.
Things for the project sponsor to consider
- Is there a clear vision for the project?
- How well does the vision align with the sponsor’s business goals, strategy and objectives?
- What high-level benefits are expected by the sponsor in undertaking the project?
- Has the sponsor got the time available and commitment to support the project?
Purpose
This phase focuses on developing an idea, assessing its fitness to proceed and providing the justification to become a project. This phase should be overseen by a sponsor working with a project manager and/or business analyst.
In this phase, the wider University support for the change is also considered.
Things to consider
- Are the necessary resources available to successfully deliver the project?
- Where is project funding going to come from?
- Are there enough benefits identified to make doing this work a good idea?
- Is the project delivering mandatory or regulatory requirements?
- Is the business area equipped to adopt the change being delivered?
- Are the risks around the change understood and clearly articulated?
Purpose
This phase focuses on ensuring that the detail of the project is understood to ensure a successful delivery. A viable business case will be developed and approved, and an assessment made on whether the business is ready for the project to begin.
Typically procurement activity also takes place in this phase.
Things to consider
- Have all internal and external, direct and indirect stakeholders been identified?
- Has the scope of the project been clearly defined and agreed?
- Have resource requirements been defined and secured?
- Have project communications been planned?
- How will the benefits be tracked and validated throughout the project?
Purpose
This phase focuses on putting the plan into action and ensuring the team stays on track to deliver the project's expected outputs and outcomes.
Things to consider
- Have project risks been captured and mitigated?
- Is the project status being reported to the portfolio and/or programme?
- Have all project decisions and changes been documented?
- Are the dependencies with other changes or projects understood?
- Is the quality of the deliverables acceptable against the agreed quality standards?
- Has the necessary testing been performed and has the agreed acceptance criteria been met?
Purpose
This phase focuses on wrapping up project activities and handing over the finished product or service to its new owner.
Things to consider
- Have the project deliverables been signed off?
- Has the handover to operations been agreed and completed?
- Have any remaining RAID items been handed over, with clear ownership and agreed timelines for monitoring and resolution?
- Have project benefits been clearly documented, with agreed timelines for them to be realised?
- Has the monitoring of benefits been handed over to the central Project Management Office (PMO) team?
Purpose
After successfully handing over the project to the teams who will use or support the project deliverables the project can be closed down.
Things to consider
- Has the project close procedure been followed?
- Has a project closure document been produced and approved by the project sponsor and project board?
- Have the lessons learned during the project been captured and shared to promote continuous improvement?
- Has a post implementation review been held to assess the delivery of the project against its original time, cost and quality objectives?
Guidance
Here is some guidance on various aspects of project management. These can be used throughout the project phases.
- Project Sponsor role description and commitment
- Product and work package breakdown structure guide
- Guide to project risk analysis and management: APM (Association of Project Management)
- Risk and issue management strategy
- Benefits realisation management process
Work is also planned to include our business analysis templates and guidance soon.
Templates
Below are some templates for each of the IT project life cycle phases. Not all templates are mandatory. Choose those which best meet the needs of the project.
More templates will be added as they are developed.
| Resource | Purpose | Project life cycle phase |
|---|---|---|
| Concept summary | Captures the initial vision, scope, risks and benefits of a project | 1. Sponsorship commitment |
| Stage-gate checklist | A checklist of tasks to complete and what to consider at each project stage-gate | 2. Concept approval |
| Business case | Provides the rationale for change, the scope, delivery methods, resources, risks, benefits and timelines | 2. Concept approval |
| Benefits profile | Captures a detailed description of a project's benefits by defining the benefit (or dis-benefit) and who is responsible for it | 2. Concept approval |
| Benefits map | A technique for understanding how a project will deliver business benefits by linking project activities to the benefits they directly impact | 2. Concept approval |
| Pre-request for authority (PRFA) | This is a finance-owned form to request approval for project expenditure | 2. Concept approval |
| Request for authority (RFA) | This is a finance-owned form to request approval for project expenditure | 2. Concept approval |
| Data protection screening tool | Ensures data protection implications of a project are understood and decides if a DPIA is required (if needed a link will be provided to the DPIA template) | 2. Concept approval |
| Cyber threat and risk assessment | Assesses the risk posed by processing activity and ensures that adequate controls are in place to secure University data (if needed a link to the assessment template will be provided) | 2. Concept approval |
| Budget workbook | A project budget template to plan and track project activity, resources and the associated costs | 3. Initiation and planning |
| Cost model | A cost model template to support modelling of project changes and the comparison of different project delivery cost options | 3. Initiation and planning |
| Communications plan | Define how stakeholders will be kept informed of project progress throughout the project life cycle | 3. Initiation and planning |
| Project board pack | A standard slide pack for a project board with optional content depending on what stage the project is at | 3. Initiation and planning |
| Project initiation document | Outlines the overall vision, objectives, outputs, delivery methods and governance for the project | 3. Initiation and planning |
| Project initiation document (lite) | A condensed version of the PID, which may be more suitable for small changes or projects delivering in a programme | 3. Initiation and planning |
| Project schedule | A Smartsheets template for a standard project plan aligned to the project phases | 3. Initiation and planning |
| RASCI matrix | A matrix to assign specific roles and responsibilities to each project member directly related to what part of the project they are working on | 3. Initiation and planning |
| RAID log | Identifies and monitor project risks, actions, issues, decisions and dependencies | 3. Initiation and planning |
| Re-request for authority (RRFA) | This is a finance-owned form to request approval for project expenditure which may have changed after a RFA has been submitted | 3. Initiation and planning |
| Status report | Monthly project update showing progress, budget snapshot and key risks and issues | 3. Initiation and planning |
| Change impact assessment | Document and agree any changes to the scope and delivery of the project | 4. Delivery |
| Benefits management plan | Identify, monitor, review and measure project/change benefits | 5. Handover |
| Project close checklist | Checklist of items to be completed for project to be closed and handed over to BAU | 5. Handover |
| Project closure report | Describes how the project achieved its objectives and delivered the capability for the project benefits to be realised | 5. Handover |